两个 arduino 间的 SPI 通信#
两个 arduino 间的 SPI 单向通信
使用中断实现 SPI Slave
连接方法是(不交叉)平行相连
Question#
SPI 库不支持做为从设备。或者说 SPI 库并没有为 arduino 作为从设备而提供简单的库函数。
How to Use SPI Communication on the Arduino - Circuit Basics
The SPI library only supports the Arduino as a master device. Because of this, pin 10 needs to be configured as an
OUTPUT, to avoid conflicts in the operation of the library.
那么怎么实现两个 Arduino 用 SPI 相互通信呢?
解决方法:使用 SPI 硬件及中断#
https://www.makerguides.com/master-slave-spi-communication-arduino/
这个例子的连线方案最简单,两个 Arduino 的通信内容分边由两边的串口内容提供,因此更容易把注意力集中在 SPI 通信上。
两个 Arduino 使用 SPI 通信,必定也是一主一从。主设备只需像原来那样使用 SPI 库,而在作为从设备的 Arduino 上,用中断来处理来自Master 的访问(包含读和写)。
通常的 SPI 外设一般只能读,或者只能写。但两个 Arduino 的 SPI 通信易于做成全双工的。
硬件连接#
在两机通信中,总是发送与接收相连,如两主机间的 UART 通信,以太网通信,都是采用交叉线接法。那么两个 SPI 是否要用交叉接线法呢?
答案是否定的,即不用交叉接线法,而是采用平行连法。要将相同编号(或名字)的引脚相连,Uno-1 的 MOSI 连接 Uno-2 的相同引脚 MOSI,Uno-1 的 MISO 连接 Uno-2 的相同引脚 MISO。
解释原因
Arduino 硬件设备有主从两种不同的工作模式,这是由内部的硬件寄存器设置实现的。在初始化阶段,Uno-2 会被设置为 Slave 模式,那么它的 MOSI 的后两个字母 SI 就是 Slave input 的意思。相对应的, Uno-1 需要设置成 Master 模式,同样用的也是 MOSI,但因为模式为 MO,所以为Master Output。这样就满足了一方是 Output,另一方是 Input 这一基本要求。
总结
在 SPI 通信中, Master 是谁很重要。在本例中, Master 是 Uno-1, Slave 是 Uno-2。所以即使用了相同的引脚,它们的功能也是不同(相反但却匹配)的。
Interfacing of two Arduino Uno Boards for SPI#
SPI Pin |
Arduino Uno-1 |
Arduino Uno-2 |
|---|---|---|
CS/SS |
10 |
10 |
MOSI |
11 |
11 |
MISO |
12 |
12 |
SCK |
13 |
13 |
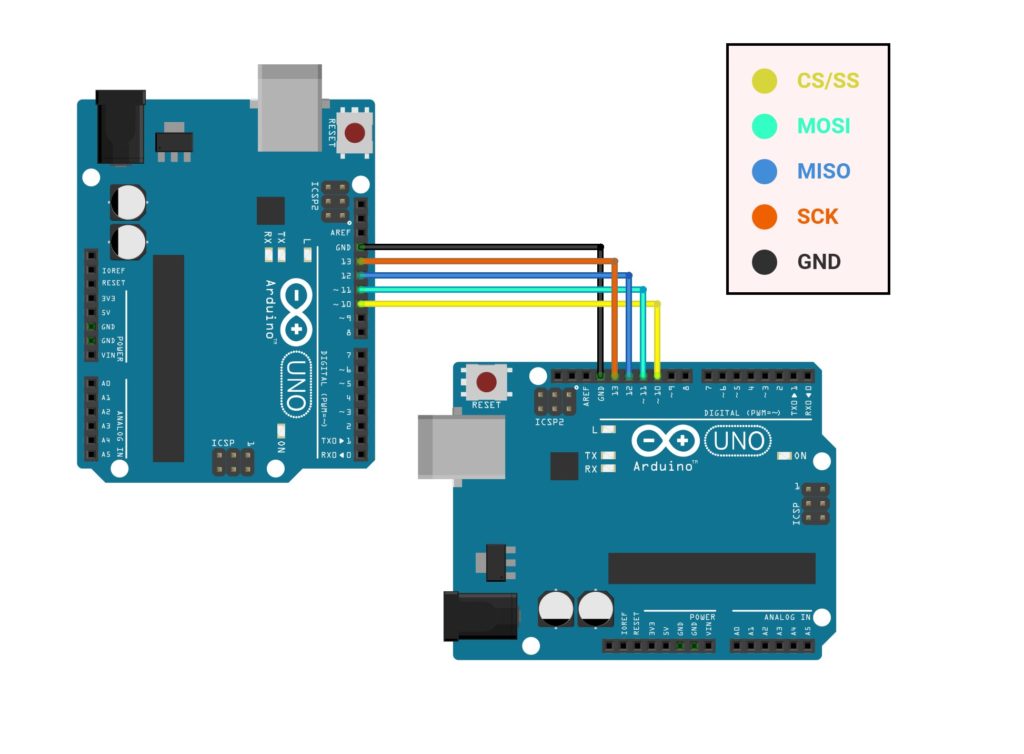
Interfacing of Arduino Uno Board and Arduino Mega Board for SPI#
SPI Pin |
Arduino UNO |
Arduino Mega |
|---|---|---|
CS/SS |
10 |
53 |
MOSI |
11 |
51 |
MISO |
12 |
50 |
SCK |
13 |
52 |
Code#
SPI Master code#
Master 的功能是通过 SPI.transfer() 每隔2秒发送一次固定的字符串消息到 Slave。
# include <SPI.h>
char str[ ]="Hello Slave, I'm Arduino Family\n";
void setup()
{
Serial.begin(115200); // set baud rate to 115200 for usart
SPI.begin();
SPI.setClockDivider(SPI_CLOCK_DIV8); //divide the clock by 8
Serial.println("Hello I'm SPI Mega_Master");
}
void loop (void)
{
digitalWrite(SS, LOW); // enable Slave Select
// send test string
for(int i=0; i< sizeof(str); i++)
SPI.transfer( str [i] );
digitalWrite(SS, HIGH); // disable Slave Select
delay(2000);
}
SPI Slave code#
Slave 的功能是:
将 MISO 设置为
设置模式为 slave
绑定 SPI 中断
在 SPI 中断服务程序中定义字符串的接收
#include <SPI.h>
char str[50];
volatile byte i;
volatile bool pin;
void setup() {
Serial.begin(115200); // set baud rate to 115200 for usart
Serial.println("Hello I'm SPI UNO_SLAVE");
pinMode(MISO, OUTPUT); // have to send on Master in so it set as output
SPCR |= _BV(SPE); // turn on SPI in slave mode
i = 0; // buffer empty
pin = false;
SPI.attachInterrupt(); // turn on interrupt
}
void loop() {
static int count;
if (pin) {
pin = false; //reset the pin
if (count++ < 5) {
Serial.print(count);
Serial.print(" : ");
Serial.println(str); //print the array on serial monitor
if (count == 5) {
delay(1000);
Serial.println("The end data");
}
}
delay(1000);
i = 0; //reset button to zero
}
}
// Interrupt function
ISR(SPI_STC_vect) {
char c = SPDR; // read byte from SPI Data Register
if (i < sizeof(str)) {
str[i++] = c; // save data in the next index in the array buff
if ((c == '\r') || (c == '\n') || (c == '\0')) //check for the end of the word
pin = true;
}
}